Ohtama Co., LTD. – Specializing in permalloy, magnetic shielding, magnetic field measurement, heat treatment and magnetic field cancellation.
Active magnetic shields (magnetic field cancellers)active_magnetic_en
About active magnetic shields (magnetic field cancellers)
In recent years, the performance of electron beam devices has increased dramatically, but this has come at the cost of increasingly strict permissible magnetic field levels. Active magnetic shields (magnetic field cancellers) are devices which enable fluctuating magnetic fields, a source of outside disturbance, to be detected to a high degree of sensitivity using 3 axis magnetic field controllers. These devices generate magnetic waves which cancel out magnetic fields using a Helmholtz coil structured along the 3 axes of XYZ, and control and stabilize the fluctuating magnetic field within the coil. The introduction of products such as these makes it possible to greatly improve the performance of electron beam devices even in unstable areas with a severe magnetic field environment.
It is also possible to mount cancellation coils on the frames of devices. This means there is no need to enlarge the area of installation for such things as semiconductor measurement and testing devices. 。

Active magnetic shields (magnetic field cancellers)
- ・Can be installed rapidly on site
- ・Do not harm the operability of electron beam devices
- ・Low cost
- ・Pleasing to the eye
- ・Can be tailored freely to the size of your choice
(Also possible to mount cancellation coils on the frames of devices)
| Main applications |
|
|---|
How to install
There are three ways to install coils: embedded in building type, installed within chamber type, and post-construction (installation on site).
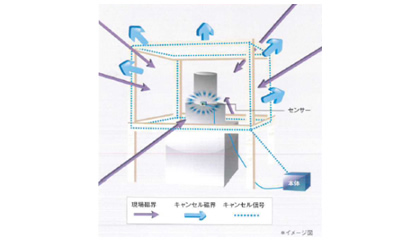
Example installation for an electron microscope
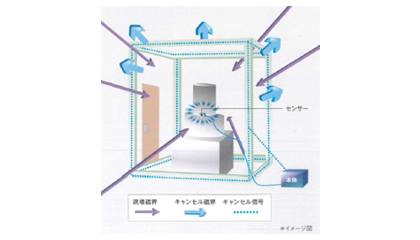
Example installation for a large electron microscope
Properties
| Independent type CA-4000 | Low noise type CA-3200 | |
|---|---|---|
| Applications | SEM/3D printers, etc. | Inside shield rooms |
| Compatible frequencies | 0Hz~180Hz | 0Hz~60Hz |
| Maximum compatible fluctuating magnetic field | 150mG(15μT) | 50mG(15μT) |
| Rate of attenuation | 33dB | 33dB |
| Control range | ±70μT | ±70μT |
| Sensor method | Flux gate method (resolving power: 5 nT) | Flux gate method (resolving power: 1 nT) |


